Epidermolysis bullosa
Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is the name for a group of rare inherited skin disorders that cause the skin to become very fragile. Any trauma or friction to the skin can cause painful blisters.
Symptoms of epidermolysis bullosa
The main symptoms of all types of EB include:
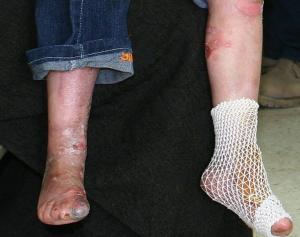
- skin that blisters easily
- blisters inside the mouth
- blisters on the hands and soles of the feet
- scarred skin, sometimes with small white spots called milia
- thickened skin and nails
Types of epidermolysis bullosa
The 3 main types of EB are:
- epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS) – the most common type, which tends to be milder with a low risk of serious complications
- dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) – which can range from mild to severe
- junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) – the rarest and most severe type
The type reflects where on the body the blistering takes place and which layer of skin is affected.
There are also many variants of these 3 main types of EB, each with slightly different symptoms.
Read more about symptoms of different types of epidermolysis bullosa.
Diagnosing EB
EB is usually diagnosed in babies and children by your neonatal team, as the symptoms are often obvious from birth. But some milder types of EB may not be diagnosed until adulthood.
If it's thought your child has the condition, they'll be referred to a skin specialist (dermatologist).
The specialist will carry out tests to find out the type of EB and help come up with a treatment plan. They may take a small sample of skin (biopsy) to send for testing.
Prenatal testing
In some cases it's possible to test an unborn baby for EB at about 11 weeks into pregnancy.
This may be offered if you or your partner are known to be a carrier of the faulty gene associated with EB and there's a risk of having a child with a severe type of EB.
If the test confirms your child will have EB, you'll be offered counselling and advice, see also more useful links below.
Prenatal tests include amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling.
Causes of epidermolysis bullosa
EB is caused by a faulty gene (gene mutation) that makes skin more fragile.
Usually, a child with EB will have inherited the faulty gene from a parent who also has EB.
It's also possible for a child with EB to have inherited the faulty gene from both parents who are just "carriers" but don't have EB themselves.
Treatment for epidermolysis bullosa
There's currently no cure for EB. Treatment aims to relieve symptoms and stop complications developing, such as infection.
A team of medical specialists will help you decide what treatment is best for your child and offer advice about living with the condition.
You can manage EB at home by:
- popping blisters with a sterile needle
- applying protective dressings
- avoiding things that make the condition worse
Medicines can be used to treat infection or to reduce pain. Surgery may be needed if EB causes narrowing of the food pipe or problems with the hands.
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA) is a form of EB with similar symptoms.
Like EB, EBA causes the skin to blister easily. It can also affect the mouth, throat and digestive tract.
But EBA isn't inherited, and symptoms don't usually appear until later life.
It's an autoimmune disease. This means your immune system starts to attack healthy body tissue. It's not known exactly what causes this.
EBA is a very rare condition that tends to affect people over the age of 40.
Support
If your child is diagnosed with EB, it can be a frightening experience. You'll probably want to find out as much as possible about the condition and available treatments, see more useful links below.
It's important not to neglect your own health and wellbeing when caring for a child with a complex condition such as EB.
- Read about Care and support and get tips on caring for a disabled child
More useful links
The information on this page has been adapted from original content from the NHS website.
For further information see terms and conditions.