Newborn screening
During the first few weeks after your baby is born, they will be offered a blood spot screening test and hearing screening test. These tests form the Northern Ireland newborn screening programmes.
Newborn hearing screening programme (NHSP)
Your baby will be offered a newborn hearing screening test shortly after birth.
The aim of this screening programme is to identify babies born with a permanent childhood hearing impairment (PCHI) at an early stage, to allow timely intervention and improved outcomes for baby.
About one to two babies in every 1,000 are born with a permanent hearing loss in one or both ears.
This increases to about one in every 100 babies who spend more than 48 continuous hours in a neonatal intensive care unit.
The person(s) with parental responsibility must consent to take part.
The screening test is carried out by a trained screener and will usually be done in the maternity unit before you go home or at an outpatient clinic, within the first few weeks following birth.
The test is painless and is usually done while baby is sleeping.
The screening test
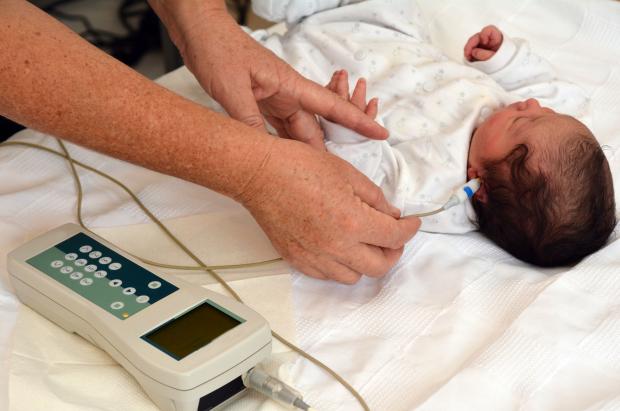
Two types of newborn hearing screening tests are provided:
- an Automated Otoacoustic Emission (AOAE) test
- an Automated Auditory Brainstem Response (AABR) test
The type of test that a baby requires and is offered, will depend on which screening protocol is applicable and the results of the initial screening test.
Automated Otoacoustic Emission (AOAE) test
The AOAE screening test involves placing a small, soft tipped earpiece in the outer part of a baby’s ear to send clicking sounds to the inner ear.
Using a computer, the screener can see how the baby’s inner ear responds to sound. (If there are no clear responses in one or both ears, following two AOAE screening tests, an AABR test is then carried out).
If clear responses are not found, the infant is referred to audiology services for diagnostic tests and further follow-up.
Automated Auditory Brainstem Response (AABR) test
An AABR is only required in certain circumstances, for example, if a baby does not have a clear response in one or both ears with AOAE testing, or has been admitted to a neonatal intensive care or special care baby unit for over 48 continuous hours.
The AABR is a different type of test that measures electrical brain activity (rather than measuring acoustic energy within the inner ear).
This screening test involves placing small sensors on a baby’s head, shoulder and nape of the neck.
Soft headphones are placed over baby’s ears and a series of clicking sounds are played.
A computer measures how the baby’s brain respond to these sounds.
The outcome of the screening test(s) will be recorded in your baby’s Personal Child Healthcare Record (PCHR or ‘red book’) and in the regional (Smart4Hearing) IT system.
Your baby’s PCHR also has a checklist of sounds your baby should react to and the types of sounds that they should make as they grow older.
Coronavirus (COVID-19)
Inpatients
If you or your baby are in hospital and are being tested, or have tested positive for COVID-19, or have symptoms associated with the virus, newborn hearing screening will be deferred and you will be offered this screening at a later date.
Outpatients
If you or your baby are being tested, or have tested positive for COVID-19, or have symptoms associated with the virus, do not go to an arranged outpatient newborn hearing screening appointment.
Contact your healthcare provider immediately to arrange a follow-up appointment.
Ongoing vigilance
If the screening test shows a clear response from both of your baby’s ears, this means that your baby is unlikely to have a permanent hearing loss.
However, the newborn hearing screening test does not pick up all types of permanent hearing loss.
In addition, children can develop a permanent hearing loss later on (after they have been screened).
Therefore, you should continue to be vigilant and check your baby’s hearing, as they grow up, using the checklist contained in the Personal Child Health Record (PCHR or 'red book’).
If you have any concerns about your baby’s hearing, at any age, you should discuss this with your health visitor or GP.
Further information about the screening programme, including leaflets, can be found on the Public Health Agency website at:
Newborn blood spot screening programme
Newborn blood spot screening is still going ahead.
However, there may be some changes to how you receive postnatal care.
You may be asked to take your baby into your local health centre or clinic for blood spot screening.
This will depend on what Trust you are from. Your midwife will discuss this with you.
In the first week after birth, all babies in Northern Ireland are offered screening for a range of inherited conditions including:
- phenylketonuria (PKU)
- congenital hypothyroidism (CHT)
- cystic fibrosis (CF)
- medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (MCADD)
- sickle cell disorders (SCD)
- maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)
- isovaleric acidaemia (IVA)
- glutaric aciduria type1 (GA1)
- homocystinuria (HCU)
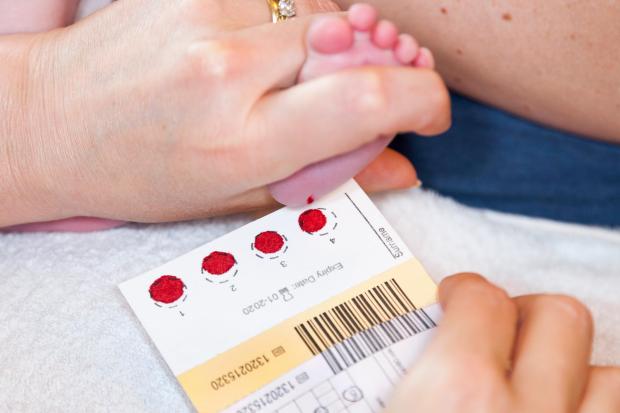
This is often called the ‘heel prick’ test.
Most babies screened will not have any of these conditions but, for the small number who do, there are a lot of benefits from screening.
The programme makes a major contribution to the prevention of disability and death, through early diagnosis and effective interventions.
It is important to let your health professional know if you, or your partner, has a family history of the conditions screened for.
Newborn blood spot screening is a complex programme, involving a wide range of services, from highly specialised laboratories through to individual staff in the community and in hospitals, working closely together.
The Public Health Agency and partner organisations are responsible for making sure that the population has access to safe, effective, high quality and equitable screening programmes.
As part of this function for newborn blood spot screening, the Northern Ireland programme takes part in a national (UK) system of quality assurance and performance management.
Further information is available in the programme leaflet:
Newborn hearing and blood spot screening are recommended.
It is also important that if, at any stage, you have any concerns about your child’s health or their hearing, you should discuss these with a health professional such as your health visitor or general practitioner.
Physical examination
All babies will be offered a routine physical examination to check their hips, heart, eyes and testes (for boys) within the first few days of life and again between six to eight weeks of age.
These examinations aim to find any health conditions or abnormalities so that any tests or treatment required can be offered to your baby as soon as possible.